This guide will explain how to use the Stanford Natural Language Parser via the Natural Language Toolkit. This allows you to generate parse trees for sentences:
Requirements
You will need the following libraries:
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 8
- Stanford Parser
- Python 2.7
- Python Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK)
Installing the JDK
- Visit Oracle’s website and download the latest version of JDK 8 for your Operating System
- Set the environment variable
JAVAHOMEto the location of your JDK. This will be somewhere like/usr/jdk/jdk1.6.0_02orC:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_02.
Note: Do not set JAVAHOME to the JDK’s \bin folder. This is not the JRE, this is the JDK.
Installing the Stanford Parser
- Download the latest version of the Stanford Parser
- Extract it to a location of your choice
- Set the environment variables
CLASSPATHandSTANFORD_MODELSto the location of the Stanford Parser. Make sure you don’t accidentally leave the Stanford Parser wrapped in another directory e.g.C:\stanford-parser\stanford-parser\[bunch of files].
Adapted from NLTK documentation
Installing Python
- Visit Python’s website
- Download the latest release of Python 2.7
- Run the installer
Installing the NLTK
- Open a command prompt with admin permissions and run
pip install nltk - You’re done (ain’t package managers grand?)
Testing your setup
To test if you’ve followed the instructions correctly run the following code (source):
import os
from nltk.parse import stanford
parser = stanford.StanfordParser()
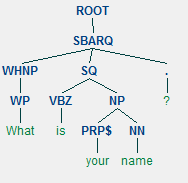
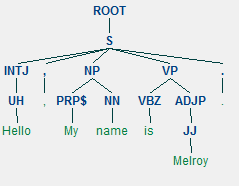
sentences = parser.raw_parse_sents(("Hello, My name is Melroy.", "What is your name?"))
print sentences
# GUI
for line in sentences:
for sentence in line:
sentence.draw()
When running the code you should see two images of parse trees. One image for each of the input sentences:
 Generated using 6 lines of Python code
Generated using 6 lines of Python code